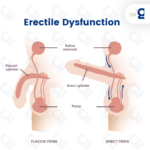
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common type of male sexual dysfunction. It is when a man has trouble getting or keeping an erection. ED becomes more common as you get older. But it’s not a natural part of aging.

Some people have trouble speaking with their doctors about sex. But if you have ED, you should tell your doctor. ED can be a sign of health problems. It may mean your blood vessels are clogged. It may mean you have nerve damage from diabetes. If you don’t see your doctor, these problems will go untreated.
Your doctor can offer several new treatments for ED. For many men, the answer is as simple as taking a pill. Getting more exercise, losing weight, or stopping smoking may also help.
What is erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is when a man cannot get or keep an erection. The condition prevents the man from having sex or finishing sex. This condition used to be called impotence. ED can occur at any age, but it is more common in men older than 75 years of age.
ED doesn’t have to be a part of getting older. As a man ages, he may need more stimulation (stroking and touching) to get an erection. He might also need more time between erections. Older men should still be able to get an erection and enjoy sex.
Symptoms of erectile dysfunction
The primary symptom of ED is not being able to get or keep an erection for sex.
What causes erectile dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by:
- Diabetes (high blood sugar).
- Hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
- Stress, anxiety, or depression.
- Alcohol and tobacco use.
- Some prescription medicines. This includes antidepressants, pain medicine, and high blood pressure medicine.
- Fatigue.
- Brain or spinal cord injuries.
- Hypogonadism (a condition that leads to low levels of the male hormone, testosterone).
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Radiation therapy to the testicles.
- Stroke.
- Some types of prostate or bladder surgery.
Problems in your relationship with your sexual partner can also cause erectile dysfunction. Improving your relationship may help your sex life. If you decide to seek therapy, it will probably be most effective if your sex partner is included.
Couples can learn new ways to please one another and to show affection. This can reduce anxiety about having erections.
Certain feelings can lead to erectile dysfunction, including:
- Feeling nervous about sex. This could be because of a bad experience or a previous episode of ED.
- Feeling stressed, including work and family stress.
- Feeling depressed.
- Feeling self-conscious about your body or performance.
- Thinking your partner is reacting negatively toward you.
How is erectile dysfunction diagnosed?
ED is usually easy to diagnose. If you are tempted to self-diagnose, talk to your doctor. He or she will want to make sure it isn’t related to another health condition.
Your doctor will do a physical exam and ask you questions about your symptoms. He or she may do a blood or urine test. Your doctor may consider other tests to rule out other conditions.
Can erectile dysfunction be prevented or avoided?
This depends on whether you know what it is causing your ED. There are some things you can do that may help prevent ED, including:
- Avoid drinking too much alcohol, smoking, or abusing drugs.
- Ask your doctor if ED is a side effect of a new or current medicine you are taking. He or she may have an alternative medicine.
- Control your blood sugar and blood pressure.
- Try to relax and avoid stress.
How do doctors treat erectile dysfunction?
Change your medicines
If a medicine you need for another health condition is causing ED, your doctor may suggest a different dose or different medicine. Never stop taking a medicine without speaking with your doctor first. Read about which medicines make it more likely that you’ll develop ED.
Prescribe medicines you take by mouth
A health care professional may prescribe you an oral medicine, or medicine you take by mouth, such as one of the following, to help you get and maintain an erection:
- sildenafil NIH external link (Viagra)
- vardenafil NIH external link (Levitra, Staxyn)
- tadalafil NIH external link (Cialis)
- avanafil NIH external link (Stendra)
All of these medicines work by relaxing smooth muscles and increasing blood flow in the penis during sexual stimulation. You should not take any of these medicines to treat ED if you are taking nitrates to treat a heart condition. Nitrates widen and relax your blood vessels. The combination can lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure, which may cause you to become faint or dizzy, or fall, leading to possible injuries.
Also talk to your health care professional if you are taking alpha-blockers to treat prostate enlargement. The combination of alpha-blockers and ED medicines also could cause a sudden drop in blood pressure.
A health care professional may prescribe testosterone NIH external link if you have low levels of this hormone in your blood. Although taking testosterone may help your ED, it is often unhelpful if your ED is caused by circulatory or nerve problems. Taking testosterone also may lead to side effects, including a high red blood cell count and problems urinating.
Testosterone treatment also has not been proven to help ED associated with age-related or late-onset hypogonadism NIH external link. Do not take testosterone therapy that hasn’t been prescribed by your doctor. Testosterone therapy can affect how your other medicines work and can cause serious side effects.
Treatment depends on what is causing it. If it is caused by uncontrolled blood sugar and high blood pressure, take your medicine and follow your doctor’s instructions.
If your doctor rules out other causes, he or she may prescribe Sildenafil (brand name: Viagra), tadalfil (brand name Cialis), and vardenafil (brand name Levitra). These medicines are taken by mouth to help you maintain an erection.
Not everyone can use these medicines. Your doctor may talk to you about alprostadil if oral medicines aren’t an option for you. Alprostadil is a synthetic version of prostaglandin E. It can be injected into the penis or inserted as a tiny suppository into the urethra (the hole at the end of the penis). Your doctor will help you decide which treatment is best for you.
Follow your doctor’s instructions when taking ED medicine. Usually, a man takes 1 tablet 30 minutes to 1 hour before he plans to have sex. Sildenafil works for 4-8 hours; vardenafil works for up to 8 hours; and tadalafil works for up to 36 hours.
You should not take more than 1 dose in 24 hours. Tadalfil and vardenafil come in tablets of 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg and 20 mg. Sildenafil comes in tablets of 25 mg, 50 mg and 100 mg.
Even if you take the medicine, you still need physical and mental stimulation and desire to have an erection. If your first dose doesn’t help, call your doctor. Your doctor may want to change your tablet strength.
The side effects of ED medicine are mostly the same. Sildenafil and vardenafil can cause:
- Headache.
- Flushing (face and upper body turning red and warm).
- Stomach upset.
- Runny nose (sniffles).
- vision changes (things look blue).
Tadalfil has the same side effects, except for the flushing and possible changes in vision. It can also cause back pain and muscle aches. For each of the medicines, headache is the most common side effect. Vision changes are the least common. Talk to your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you.
Call your doctor right away if you take one of these medications and have a prolonged erection that lasts 4 hours or longer. This condition may cause permanent impotence if not treated.
Can everyone use ED medications?
You shouldn’t use these medicines if you take nitroglycerin or any other nitrates for chest pain. If you have heart problems, tell your doctor before taking any ED medicines. These medicines can have serious side effects in people who have heart problems.
If you use sildenafil, tadalfil, or vardenafil and get chest pains, be sure to tell the paramedics, nurses or doctors at the hospital that you use it and when you used it last.
Living with erectile dysfunction
If the medicines aren’t right for you, you could try using a penile implant, vacuum pump devices, or have surgery. Your doctor may send you to a urologist to talk about these options.
How will side effects of erectile dysfunction medicines affect me?
ED medicines that you take by mouth, through an injection, or as a pellet in the urethra can have side effects, including a lasting erection known as priapism. Call a health care professional right away if an erection lasts 4 hours or longer.
A small number of men have vision or hearing loss after taking oral ED medicines. Call your health care professional right away if you develop these problems.
Prescribe a vacuum device
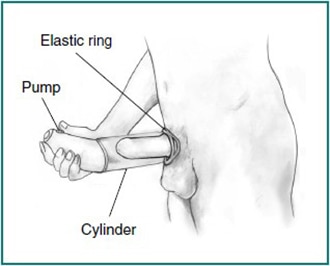
A vacuum device causes an erection by pulling blood into the penis. The device has three parts:
- a plastic tube, which you put around your penis
- a pump, which draws air out of the tube, creating a vacuum
- an elastic ring, which you move from the end of the tube to the base of your penis as you remove the tube
The elastic ring maintains the erection during intercourse by preventing blood from flowing back into your body. The elastic ring can remain in place up to 30 minutes. Remove the ring after that time to bring back normal circulation and to prevent skin irritation.
You may find that using a vacuum device requires some practice or adjustment. Using the device may make your penis feel cold or numb and have a purple color. You also may have bruising on your penis. However, the bruises are most often painless and disappear in a few days. Vacuum devices may weaken ejaculation but, in most cases, the devices do not affect the pleasure of climax, or orgasm.